Dispute Resolution and Legal Remedies
When disagreements arise over an insurance claim or policy terms, knowing how to resolve these disputes effectively is crucial. As a policyholder, you have rights and avenues to address issues with your insurance provider. Whether it’s a disagreement over claim payouts, coverage interpretations, or contract terms, exploring your options for dispute resolution and understanding legal remedies can help ensure a fair outcome.
Common Insurance Disputes
Disputes with an insurance provider can cover a wide range of issues, such as:
- Claim Denial: The insurer denies your claim, citing policy exclusions or lack of evidence.
- Disagreement on Payout Amount: The insurer approves your claim but offers a settlement amount you find insufficient.
- Coverage Disputes: Confusion arises over whether a specific event or damage is covered by your policy.
- Policy Cancellation: Your insurer cancels your policy, and you believe the action was unjustified or unsubstantiated.
Understanding your dispute type helps determine the most suitable resolution process to pursue.
Methods for Resolving Insurance Disputes
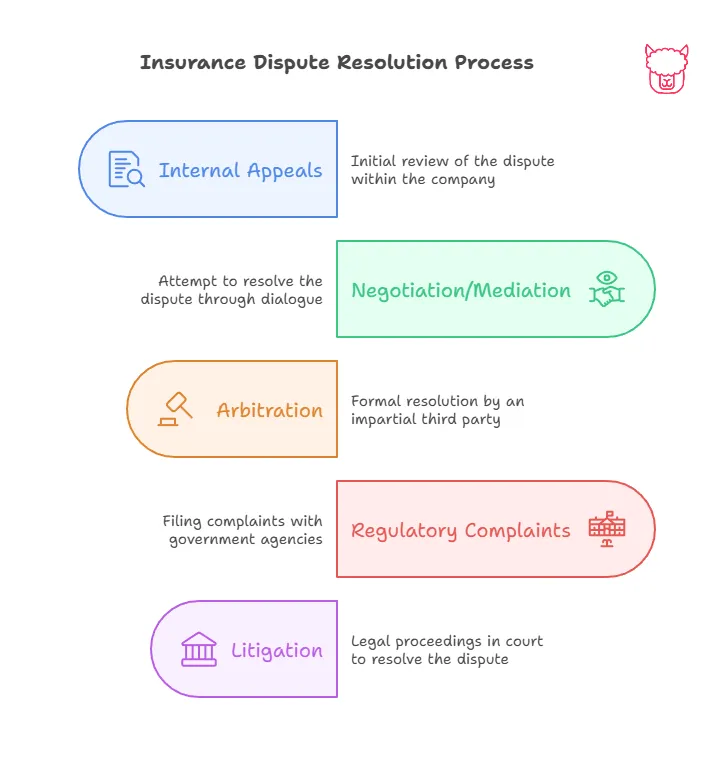
1. Internal Appeals
Before pursuing external options, most insurers provide an internal appeals process.
- What It Involves: You formally request your insurer to review its decision.
- Process:
- Obtain the denial letter or written explanation of the insurer’s position.
- Gather supporting documentation (e.g., receipts, photographs, expert opinions).
- Submit an appeal and request a reconsideration.
- Timeframe: Insurers are required to process appeals promptly, typically within 30–60 days.
2. Negotiation and Mediation
If the internal appeal does not yield the desired results, consider negotiation or mediation.
- Negotiation: A direct discussion with the insurance company to reach a fair compromise. Bringing evidence to support your case—like policy details, inspection results, and expert evaluations—can strengthen your position.
- Mediation: A neutral third party facilitates the discussion to help both parties reach a mutually agreeable resolution. Mediation is voluntary and non-binding, making it a less adversarial option.
3. Arbitration
Arbitration is a formal process where a neutral arbitrator reviews the dispute and makes a decision.
- Voluntary or Mandatory: Some insurance policies include mandatory arbitration clauses, while others make it optional.
- Binding vs. Non-Binding: With binding arbitration, the arbitrator’s decision is final. In non-binding arbitration, the decision serves as a recommendation.
- Key Advantage: Arbitration is usually faster and less expensive than litigation.
4. Filing a Complaint with Regulators
If you feel your insurer has acted in bad faith or violated insurance laws, you can file a formal complaint with your state’s insurance department.
- What They Do: Regulatory bodies investigate consumer complaints, enforce compliance, and resolve disputes between policyholders and insurers.
- How to File: Most state insurance departments allow online complaint submissions. Document all interactions with the insurer to support your claim.
5. Litigation (Filing a Lawsuit)
When other methods fail or if you suspect bad faith, filing a lawsuit may be necessary.
- When to Consider: Litigation is a last resort because it is time-consuming and costly. It’s typically pursued in cases involving:
- Alleged insurance fraud
- Breach of contract
- Bad faith practices by the insurer
- Consult Legal Counsel: An experienced insurance lawyer can evaluate your case and guide you through the process.
Legal Remedies for Insurance Disputes
If you pursue litigation or arbitration, several legal remedies may apply:
-
Claim Payment: The court or arbitrator orders the insurer to pay the claim amount owed.
-
Interest and Penalty Awards: Insurers that delay payment without valid grounds may be required to pay additional interest or penalties.
-
Attorney Fees and Costs: You may be compensated for legal fees incurred during the dispute process, depending on state laws and judgment outcomes.
-
Compensatory Damages: If you suffered financial harm due to the insurer’s actions, you may be awarded damages to make you financially whole.
-
Punitive Damages: In cases of insurer bad faith or egregious misconduct, courts may impose punitive damages to deter similar behavior in the future.
Tips for Policyholders During Disputes
- Know Your Policy: Review your insurance policy thoroughly to understand your rights and obligations. Pay special attention to exclusions, conditions, and dispute resolution clauses.
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed documentation of all communications with your insurer. Include dates, times, and names of contact persons.
- Act Swiftly: Resolve disputes promptly to avoid policy lapses and further complications.
- Seek Expert Advice: Consider consulting professionals, such as insurance adjusters, appraisers, or legal counsel, for guidance.
Conclusion
Insurance disputes can be stressful, but they don’t have to feel overwhelming. Exploring available resolution methods—such as internal appeals, mediation, or arbitration—can often resolve disagreements without escalating to litigation. Policyholders should also understand their legal remedies if disputes cannot be resolved amicably. By staying informed and taking a proactive approach, you can protect your rights and ensure a fair resolution with your insurance provider.
For further assistance, consider reaching out to your state insurance regulatory body or consulting an attorney who specializes in insurance law. Always remember: Paca Insurance is here to guide you every step of the way!
Next Steps
To build on your understanding of dispute resolution and legal remedies, we recommend exploring the following sections from the Policyholder’s Handbook. These topics can help deepen your knowledge and provide additional tools for navigating insurance-related issues effectively:
-
Your Rights as a Policyholder
Learn about the protections available to you as an insurance policyholder, including transparency requirements, dispute resolution rights, and fair treatment standards. -
The Claims Investigation Process
Gain insight into how insurers investigate claims, what steps are involved, and how to prepare effectively to ensure a smooth claims process. -
Exclusions and Limitations
Understand the fine print in your insurance policy, particularly what is not covered, to avoid disputes and ensure you’re fully informed about your coverage. -
Appeals and Dispute Resolution
Explore more about the specific steps involved in resolving claim disputes and appealing insurer decisions to advocate for a fair settlement. -
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance
Familiarize yourself with the role of regulatory authorities and how they enforce insurance compliance to protect your rights as a consumer.