Coverage Details: Understanding the Fundamentals of Insurance
Insurance coverage is a safety net that provides financial protection against unexpected events. However, understanding the key elements of insurance coverage—such as limits, deductibles, policy periods, premiums, endorsements, and exclusions—can help you make informed decisions when selecting, managing, or renewing a policy. This guide breaks down these insurance fundamentals in simple, easy-to-understand terms.
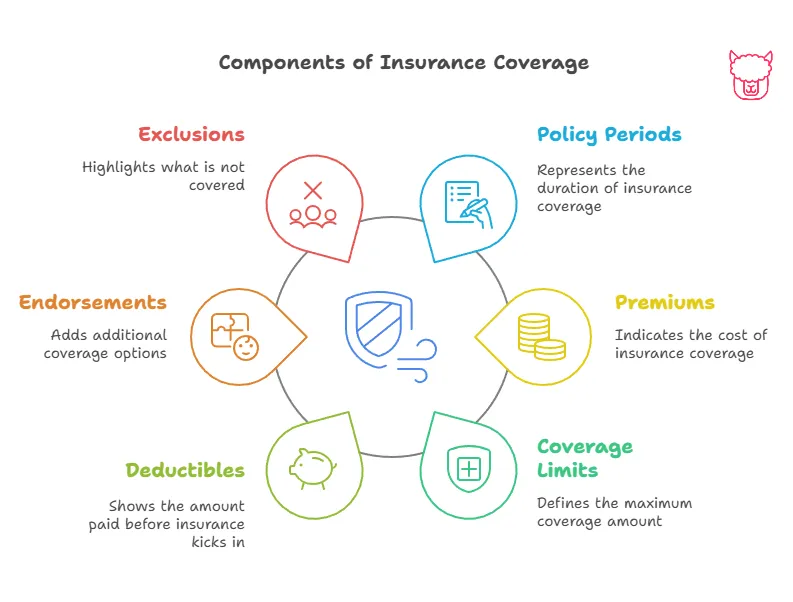
1. Coverage Limits
Coverage limits refer to the maximum amount an insurance company will pay for a covered claim under your policy. These limits vary based on the type of insurance and the terms of the policy.
- Types of Limits:
- Per-Occurrence Limit: The maximum payout for a single claim.
- Aggregate Limit: The total maximum payout for all claims during a policy period.
Why It Matters:
If a claim exceeds the coverage limit, you may be responsible for paying the remaining costs out of pocket. It’s essential to select limits that reflect your needs and provide adequate protection for your assets.
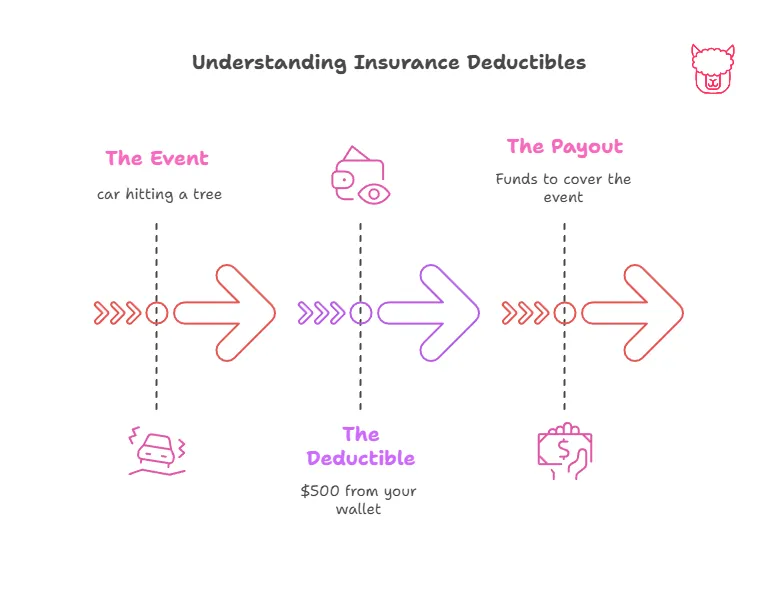
2. Deductibles
A deductible is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. For example, if you have a $500 deductible and a claim for $2,000, you’ll pay the first $500, and the insurer will cover the remaining $1,500.
- Types of Deductibles:
- Fixed Dollar Amount: A set dollar figure, such as $500 or $1,000.
- Percentage-Based Deductibles: Typically used for high-value properties or disaster coverage, calculated as a percentage of the insured value.
How Deductibles Impact You:
Higher deductibles can lower your premiums, making your policy more affordable. However, you should always choose a deductible you can comfortably afford in case of a claim.
3. Policy Periods
A policy period is the length of time your insurance policy is in effect. Common durations are six months or one year, after which the policy must be renewed.
- Key Dates to Know:
- Effective Date: When the coverage begins.
- Expiration Date: When the coverage ends unless renewed.
Why It’s Important:
It’s critical to ensure your coverage does not lapse. A lapse in coverage can leave you financially vulnerable and may result in higher premiums when you renew.
4. Premiums
A premium is the amount you pay—usually monthly, quarterly, or annually—for your insurance policy. Several factors influence your premium amount, including:
- Coverage Type and Limits: Higher coverage limits and lower deductibles generally result in higher premiums.
- Risk Factors: Your personal and property risk profile, such as driving history, location, or age.
- Claims History: A history of frequent claims might increase premiums.
Managing Premium Costs:
Consider bundling multiple policies (such as auto and home insurance) with the same provider for discounts or taking proactive steps to reduce risks, like installing a security system in your home.
5. Policy Endorsements
Policy endorsements—also known as riders—are add-ons or modifications to your base policy that provide additional coverage or adjust terms to meet specific needs.
- Examples of Common Endorsements:
- Adding coverage for high-value items (jewelry, art, or collectibles).
- Extending coverage for events like natural disasters.
- Adjusting policy terms to reflect lifestyle changes, such as adding a teen driver to an auto insurance policy.
Benefits of Endorsements:
They allow you to customize your policy for more comprehensive protection while ensuring you only pay for the coverage you truly need.
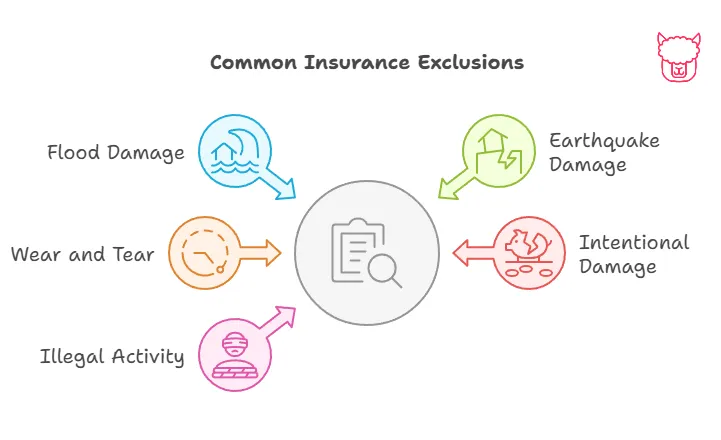
6. Exclusions
Exclusions outline what is not covered under your insurance policy. These are specific risks, losses, or events for which the insurer will not provide benefits.
- Common Exclusions:
- Natural disasters like floods or earthquakes (unless a separate policy is purchased).
- Intentional damage or illegal activities.
- Wear and tear, such as the gradual deterioration of a home or vehicle.
How to Navigate Exclusions:
Always review your policy documents carefully to understand exclusions. If necessary, purchase additional coverage, such as flood or earthquake insurance, to fill in the gaps.
Summary of Key Takeaways:
- Coverage Limits: Choose limits that reflect your financial needs and protect your assets.
- Deductibles: Opt for a deductible that balances affordability and protection.
- Policy Periods: Keep a close eye on renewal dates to avoid lapses in coverage.
- Premiums: Understand what factors influence your premium rates and explore ways to save.
- Endorsements: Use endorsements to customize your policy based on your specific needs.
- Exclusions: Be aware of what your policy doesn’t cover and consider supplementary coverage if necessary.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the intricacies of your insurance coverage is essential for protecting yourself, your loved ones, and your assets effectively. At Paca Insurance, we’re committed to helping you navigate the complexities of insurance with clarity and confidence. If you have any questions about your policy or need assistance tailoring your coverage, don’t hesitate to reach out to your insurance agent.
By keeping these fundamentals in mind, you’ll be well-prepared to make informed insurance choices that align with your goals and financial situation!
Next Steps
To continue deepening your understanding of insurance and making the most of your policy with Paca Insurance, we recommend the following sections of the Policyholder’s Handbook:
-
The Role of Insurance in Risk Management
Learn how insurance acts as a critical element in managing and mitigating financial risks. Build a strong foundation in understanding how insurance integrates into broader risk strategies. -
Types of Insurance Policies
Curious about different kinds of insurance coverage? This section provides an overview of the various policy options available, from personal insurance to specialized business coverage. -
Exclusions and Limitations
Take a closer look at what’s not covered by your policy and how exclusions can affect your coverage. This guide highlights common scenarios to help you avoid surprises. -
Tips for a Smooth Claims Experience
Looking to file a claim? This resource provides best practices and practical advice to help ensure a seamless claims process. -
Utilizing Insurance as Part of a Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
Discover how insurance fits into a well-rounded risk management strategy to protect yourself, your family, or your business more effectively.