Car Insurance
If you're in an accident
Accident happens
Ensure safety and exchange info
Report claim to carrier/agent
Repair or settlement
Follow-up and claim closure
Car insurance is an essential safeguard for anyone who owns or drives a vehicle, offering financial protection in case of accidents, damages, or other unforeseen events. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how car insurance works, the types of coverage available, legal and financial requirements, and optional add-ons you might consider to suit your needs.
Who this helps (at a glance)
- New drivers and families adding teen drivers
- Daily commuters and rideshare users
- Households with financed/leased vehicles (lienholder requirements)
- Anyone wanting clear, predictable out‑of‑pocket costs after a loss
State specifics at a glance
- Minimum liability varies by state (e.g., 25/50/25). Proof of insurance is required; penalties apply if you lapse.
- Some states use no‑fault rules (PIP) and may require UM/UIM.
- Always verify details with your state DMV/DOT and Department of Insurance.
Use Paca to manage auto in minutes
- Upload your current auto policy — we extract limits, deductibles, and endorsements automatically.
- Run the Savings & Coverage Scan — see typical limit ranges and potential savings before renewal.
- Turn on Renewal Alerts — avoid lapses; get proactive reminders and evidence checklists.
- Export a claim prep checklist — photos, police report, receipts, and contacts in one place.
- Keep everything organized — all policies, renewals, and actions in one login.
What Is Car Insurance?
At its core, car insurance is a contract between you and an insurance provider. In exchange for a premium, the insurer agrees to cover specified losses or damages related to your vehicle or liability. This coverage serves as a financial safety net, protecting you from the high costs associated with accidents, theft, or other incidents.
Why Is Car Insurance Important?
Car insurance is not just a legal requirement in most states but also a critical component of responsible vehicle ownership. It helps:
- Protect your finances: Covers repair costs, medical expenses, and liability claims.
- Ensure legal compliance: Meets the minimum insurance requirements mandated by your state.
- Provide peace of mind: Offers assurance that you’ll be supported financially in case of an accident or damage.
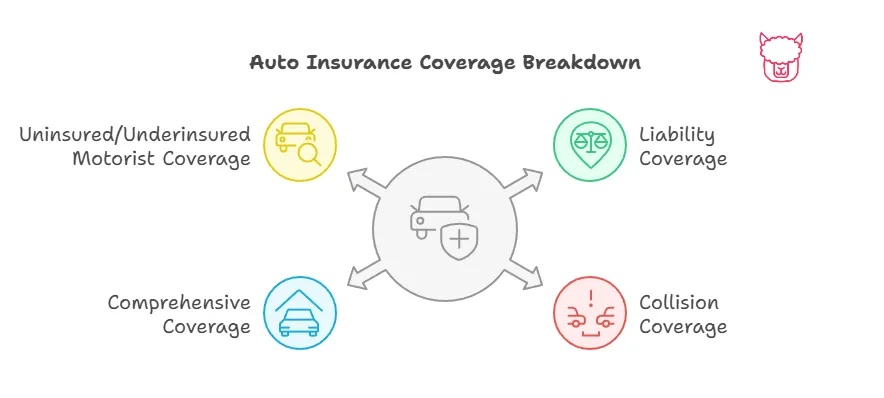
Types of Car Insurance Coverage
Car insurance policies typically consist of several individual coverages, each addressing different aspects of protection.
1. Liability Coverage (Required in Most States)
- Bodily Injury Liability: Covers medical expenses and legal fees if you’re responsible for an accident that injures others.
- Property Damage Liability: Pays for repair or replacement of property damaged by your vehicle, such as another car, fences, or buildings.
2. Collision Coverage
- Pays for damage to your own vehicle caused by a collision, regardless of who is at fault. This is especially critical if your car is financed or leased.
3. Comprehensive Coverage
- Protects against non-collision-related incidents, such as theft, vandalism, weather damage (hail, floods), or hitting an animal.
4. Personal Injury Protection (PIP) or Medical Payments Coverage (MedPay)
- Covers medical expenses for you and your passengers after an accident, regardless of fault. PIP may also include lost wages and rehabilitation costs.
5. Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
- Protects you if you’re involved in an accident with a driver who has inadequate or no insurance.
6. Optional Add-Ons
Depending on your needs, you can enhance your policy with optional features:
- Roadside Assistance: Covers towing, jump-starts, and flat tire repair.
- Gap Insurance: Pays the difference between the car’s actual cash value and the amount you owe on a loan or lease.
- Rental Car Coverage: Reimburses you for the cost of a rental car while your vehicle is being repaired.
- Custom Equipment Coverage: Covers modifications or aftermarket additions.
State Requirements for Car Insurance
Each state in the U.S. sets minimum insurance requirements for drivers. These typically focus on liability coverage and may include specific limits for bodily injury and property damage. Here’s what you need to know:
- Minimum Liability Limits: Often represented as numbers (e.g., 25/50/25), which stand for:
- $25,000 per person for bodily injury.
- $50,000 per accident for bodily injury to multiple people.
- $25,000 per accident for property damage.
- Proof of Insurance: Drivers must carry proof of insurance while driving and show it when requested by law enforcement or during an accident.
- No-Fault States: Some states require Personal Injury Protection (PIP) coverage as part of their no-fault insurance laws.
Failure to meet these requirements can result in fines, license suspension, or other penalties.
Factors Influencing Car Insurance Premiums
Car insurance premiums are calculated based on a variety of personal and vehicle factors, such as:
- Driving history: Accidents, tickets, and violations may increase rates.
- Vehicle type: Luxury or sports cars may cost more to insure.
- Location: Urban areas often have higher rates due to increased accident and theft risks.
- Usage: Driving frequently or using your car for business purposes may lead to higher premiums.
- Credit score: In some states, a higher credit score may lead to lower rates.
Additionally, bundling multiple policies (e.g., car and home insurance) or maintaining a clean driving record can help you qualify for discounts.
How to Choose the Right Car Insurance Policy
When selecting an car insurance policy, here are a few key considerations:
-
Assess Your Needs:
- Do you commute frequently? Consider collision and comprehensive coverage.
- Do you live in a high-risk area for theft? Comprehensive insurance is critical.
-
Understand State Requirements:
- Research your state’s minimum coverage mandates and ensure compliance.
-
Evaluate Coverage Limits:
- Don’t just settle for the minimum. Higher liability limits can provide additional protection in major accidents.
-
Compare Quotes:
- Shop around and compare policies from multiple providers to identify opportunities for savings.
-
Read the Fine Print:
- Understand what each policy does and does not cover. Pay attention to exclusions and deductibles.
Conclusion
Car insurance is more than just a legal obligation—it’s a financial safety net that shields you and others from the high costs associated with accidents, injuries, and damages. By understanding the different types of coverage, fulfilling your state’s requirements, and customizing your policy to fit your needs, you can ensure you’re adequately protected on the road.
Don’t wait until it’s too late—review your current policy, assess your coverage needs, and reach out to Paca Insurance to explore flexible car insurance options that fit your budget. With the right plan in place, you can drive confidently, knowing you’re prepared for whatever the road ahead may bring.
For assistance or to get a personalized quote, contact us today!
Related reading
To expand your understanding of car insurance and explore related topics crucial for informed decision-making, we recommend the following sections from the Policyholder’s Handbook:
-
The Role of Insurance in Risk Management
Learn how car insurance integrates into broader risk management strategies, ensuring financial stability and preparedness for unforeseen events. -
Understanding Coverage Limits
Dive deeper into the concept of policy limits, their significance, and how they affect your car insurance coverage. This section explains how to choose the right limits tailored to your needs. -
When and How to File a Claim
Accidents and damages happen—this guide provides step-by-step instructions to navigate the claims process effectively, ensuring a smooth experience. -
Reporting Insurance Fraud
Protect yourself and others by understanding how to identify and report fraudulent activities that can impact claim filings and premiums. -
Types of Insurance Policies
Broaden your knowledge by exploring other types of personal insurance policies, such as homeowners or life insurance, to see how they complement your car insurance policy.
References
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) — https://www.nhtsa.gov/
- Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) — https://www.iihs.org/
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) — https://www.naic.org/
- USA.gov — Motor vehicle services (state links) — https://www.usa.gov/motor-vehicle-services