Premiums: How They're Calculated
Insurance premiums are the foundation of every insurance policy, representing the cost policyholders pay to receive coverage. This payment ensures that the insurance provider can cover claims when the unexpected happens. However, the process of calculating premiums is complex and influenced by numerous factors that insurance companies consider to assess risk and determine the cost. In this article, we will break down how premiums are calculated, the factors that affect pricing, and the payment options available to policyholders.
What Are Insurance Premiums?
Insurance premiums are the fees paid by individuals or businesses to maintain an active insurance policy. Depending on the type of policy, premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, semiannually, or annually. For the insurer, premiums serve as revenue to cover claim payouts, administrative costs, and risk pooling for policyholders.
How Are Premiums Calculated?
Insurance companies use actuarial science, a combination of mathematics, statistics, and data analysis, to determine premium rates. These calculations are based on the level of risk associated with insuring a specific individual, asset, or business. Here is a step-by-step look at how premiums are determined: \
1. Risk Assessment
The cornerstone of premium calculation is evaluating the risk you (as the policyholder) pose to the insurer. The likelihood of filing a future claim plays a significant role in pricing. Factors such as your behavior, health, age, location, or even business practices can increase or decrease your perceived risk.
2. Underwriting Process
Insurers use the underwriting process to refine their understanding of your risk profile. During underwriting:
- Information is gathered from your application, prior history, and external sources (like driving records or credit scores).
- Categorizing risk levels (low, medium, or high) helps establish what your premium rate will look like.
3. Base Premium Rates
Insurers set base premium rates as a starting point for each product or policy. These rates reflect the average cost of insuring a specific category, such as auto insurance for middle-aged drivers or homeowners insurance in a specific ZIP code.
4. Adjustments for Personal or Business-Specific Factors
Base rates are adjusted upward or downward based on details specific to the policyholder. For example:
- A clean driving history might reduce auto insurance premiums, while multiple speeding tickets can increase them.
- A home equipped with security systems may lower homeowners insurance premiums.
- Younger drivers or businesses operating in high-risk industries will often see higher premiums.
5. Insurance Coverage Choices
The premiums quoted for your insurance depend on the following policy variables you select:
- Coverage Limits: Higher limits provide more protection but also result in higher premiums.
- Deductibles: Opting for a higher deductible (the amount you pay out of pocket before the insurer covers a claim) can reduce your premium.
- Optional Riders or Endorsements: Customizing your policy with riders like flood insurance or business interruption coverage adds to the premium cost.
Factors That Influence Insurance Premiums
While calculation methods vary by the type of insurance, several general factors consistently influence premium costs:
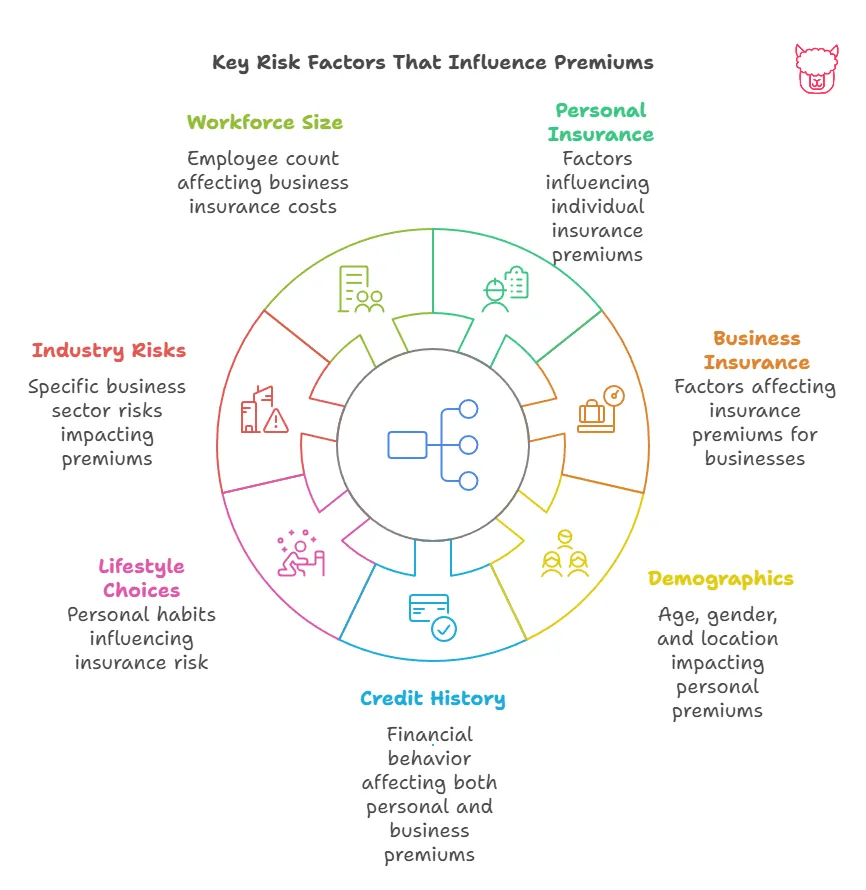
Personal Insurance
- Demographics: Factors like age, marital status, gender, and occupation often play a role in personal insurance pricing, such as health or auto insurance.
- Credit History: A strong credit score is often linked to lower premiums, as it signals financial responsibility.
- Claims History: A history of frequent claims can indicate higher risk, leading to higher premiums.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, risky hobbies (e.g., skydiving), or driving habits can increase risk levels.
Business Insurance
- Industry Risks: Businesses in high-risk industries, like construction or manufacturing, pay higher premiums compared to lower-risk sectors like consulting.
- Workforce Size and Risk: The number of employees and the nature of their work impact premiums for workers’ compensation insurance.
- Location: Businesses in areas prone to natural disasters, theft, or accidents may face heightened premiums.
Payment Options for Premiums
To make premium payments more manageable, insurers typically offer a range of flexible payment options:
- Installment Payments: Most insurers offer monthly, quarterly, or semiannual payment plans, though these may include small fees.
- Annual Payment: Paying your premium upfront for the entire year often comes with discounts.
- Bundled Payments: Combining multiple policies—such as auto and homeowners insurance—in a bundle often results in cost savings.
Modern payment conveniences include online payment portals, automatic deductions, and mobile app integrations, making it easier than ever to keep up with your premiums.
Managing Premium Costs
Although premiums are determined largely by risk, there are a few actionable strategies to help you manage costs:
- Shop Around: Compare quotes from multiple insurers to find competitive rates.
- Improve Risk Factors: Actions like maintaining a good credit score, investing in safety measures for your home or business, and driving safely can lower your risk profile.
- Select Higher Deductibles: If you can afford more out-of-pocket costs, consider a higher deductible to limit your premium.
- Use Discounts: Check for discounts related to bundling, securing your home, safe driving, or loyalty programs.
Conclusion
Premiums are designed to reflect the unique risks you bring to the table, as well as the coverage choices you make. By understanding the detailed calculations behind premium pricing—ranging from risk assessment, underwriting, and policy customizations—you can take proactive steps to lower your costs while ensuring you have the right coverage.
Managing your premiums effectively starts with being informed. Evaluate your policies regularly, keep communication open with your insurance agent, and ensure your coverage aligns with your life’s needs. Being proactive not only helps you control costs but also ensures peace of mind when the unexpected happens.
For more personalized guidance on premiums and pricing strategies, contact Paca Insurance today—your trusted partner in risk management.
Next Steps
To deepen your understanding of insurance concepts and make informed choices about your coverage, here are some recommended sections in the Policyholder’s Handbook that align with the topic of premiums:
-
How Insurance Works: Premiums, Claims, and Payouts
Explore the foundational mechanics of insurance, focusing on premiums’ role in the overall insurance process, from paying claims to ensuring financial solvency for the insurer. -
Understanding Coverage Limits
Learn how coverage limits influence your premium costs and how to balance adequate protection with affordability when selecting your policy limits. -
Deductibles: What They Are and How They Affect You
Dive deeper into the concept of deductibles, how they impact premiums, and strategies for choosing the right deductible level for your circumstances. -
Policy Endorsements and Customization
Understand how optional riders and policy modifications can affect your premium calculations and help you tailor your coverage to meet specific needs. -
The Role of Insurance in Risk Management
Gain insights into how insurance fits into your broader risk management plan and how thoughtful choices about coverage and premiums can help mitigate financial risks.